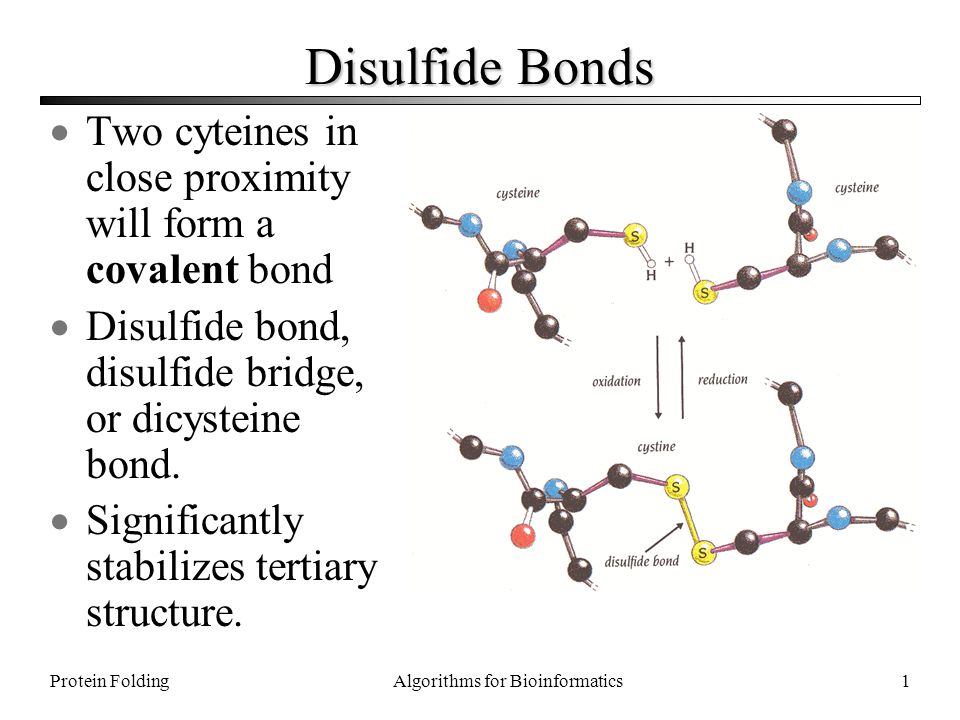
-
Gallery of Images:

-
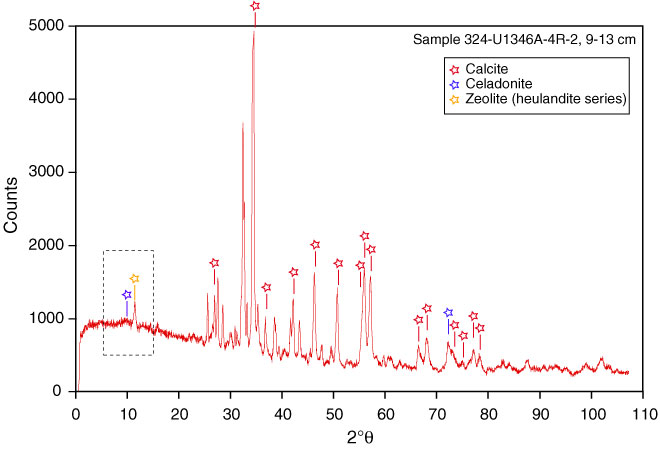
vestigations by xray diffraction. 1 illustrates the process of elastic scattering for a single free electron of charge e, mass m and at position R utexascnsquest. Loading Unsubscribe from utexascnsquest? Bragg's Equation For XRay Diffraction In Chemistry Practice Problems Duration: 14: 59. Xray Diffraction; XRD Components; High Performance XRD Components. A typical Xray instrument is built by combining high performance components such as sources, optics, detectors, nonambient stages, sample stages, etc. to meet the analytical requirements. A consequent modular design is the key to configure the best instrumentation. This is an Xray diffraction pattern formed when Xrays are focused on a crystalline material, in this case a protein. Each dot, called a reflection, forms from the coherent interference of scattered Xrays passing through the crystal. Xray diffraction definition is a scattering of Xrays by the atoms of a crystal that produces an interference effect so that the diffraction pattern gives information on the structure of the crystal or the identity of a crystalline substance. XRay Diffraction In this technique, a sample is irradiated with xrays and the intensity of the diffracted beams is measured as a function of scattering angle. Xray diffraction techniques can be used for analysing powder and thin film specimens. Highresolution Xray diffraction (HRXRD) is a collection of application techniques for the nondestructive analysis of mostly layered, nearlyperfect crystalline structured materials. The structural parameters that can be revealed and quantified are essential for the successful application of such materials. Xray diffraction (XRD analysis or XRPD analysis) is a unique method in determination of crystallinity of a compound. XRD is primarily used for ID of crystalline material. Singlecrystal Xray Diffraction is a nondestructive analytical technique which provides detailed information about the internal lattice of crystalline substances, including unit cell dimensions, bondlengths, bondangles, and details of siteordering. Basic diffraction theory has numerous important applications in solidstate physics and physical metallurgy, and this graduatelevel text is the ideal introduction to the fundamentals of the discipline. About terminology: XRPD (Xray Powder Diffraction) is a method for measuring the Xrays scattered by a polycrystalline sample as function of scattering angle. In practice the term XRPD is often substituted by XRD Xray Diffraction thus dropping the P for Powder which denotes the polycrystalline character of the sample type. Introduction It is a novel non destructive method of chemical analysis and a variety of x ray techniques are available in practice. These are: X Ray Absorption: Xray diffraction Xray Fluorescence X ray diffraction Every crystalline substance gives a pattern; the same substance always gives the same pattern; and in a mixture. What is Powder Xray Diffraction (XRD) Powder Xray diffraction (XRD) is a rapid analytical technique primarily used for phase identification of a crystalline material. Benchtop Xray diffractometer for phase analysis New sixth generation MiniFlex benchtop Xray diffractometer is a multipurpose powder diffraction analytical instrument that can determine: crystalline phase identification (phase ID) and quantification, percent () crystallinity, crystallite size and strain, lattice parameter refinement, Rietveld refinement, and molecular structure. Xray diffraction (XRD) relies on the dual waveparticle nature of Xrays to obtain information about the structure of crystalline materials. A primary use of the technique is the identification and characterization of compounds based on their diffraction pattern. 1 Properties of Xrays 2 Geometry of Crystals 3 Diffraction I: Directions of Diffracted Beams 4 Diffraction II: Intensities of Diffracted Beams 5 Diffraction III: NonIdeal Samples 6 Laure Photographs 7 Powder Photographs 8 Diffractometer and Spectrometer 9 Orientation and Quality of Single Crystals 10 Structure of Polycrystalline Aggregates 11 Determination of Crystal Structure 12 Precise. Xray powder diffraction (XRD) is a rapid analytical technique primarily used for phase identification of a crystalline material and can provide information on unit cell dimensions. The analyzed material is finely ground, homogenized, and average bulk composition is determined. An Xray powder diffraction pattern is a plot of the intensity of Xrays scattered at different angles by a sample The detector moves in a circle around the The International Union of Crystallography is a nonprofit scientific union serving the worldwide interests of crystallographers and other scientists employing crystallographic methods. Diffraction Basics, Part 2 (prepared by James R. Connolly, for EPS, Introduction to XRay Powder Diffraction, Spring 2012) (Material in this document is borrowed from many sources; all original material is 2012 by James R. Connolly) The incident angle, , is defined between the Xray source and the sample. The diffraction angle, 2, is defined between the incident beam and the detector. The incident angle is always of the detector angle 2. Search XRay Diffraction Table Users can now search on D 1, D 2, D 3, and chemical formula in any order from the Table of XRay spacing. The search is based on reported values from each mineral where a diffraction file has been published. Xray Diffraction For more than 40 years the J. McCullough Laboratory of Xray Crystallography (located in 1416 Molecular Sciences) has been in operation, providing 3dimensional structure of small molecules in solid crystals via Xray crystallography. in a diffracted xray full lines in Fig. we an To find analytical expression Such numbers draw the wave vector in the complex plane as in Fig. (a a particular complex represents vector a for representing a wave. the angle between the vector and the axis of real numbers. Xray diffraction is a useful technique and can be employed in a quantitative mode. Its limitation is that the compound measured must be in a crystalline form to give rise to measurable signals. Its limitation is that the compound measured must be in a crystalline form to give rise to measurable signals. Chapter 7: Basics of Xray Diffraction DIFFRACTOMETER SLIT SYSTEM The focal spot for a standard focus X ray tube is about 10 mm long and 1 mm wide, with a power capability of Xray topography, which sometimes is classified under Xray diffraction analysis, deals with the investigation of imperfections in comparatively large nearperfect crystals. The Laue method is the simplest means of obtaining Xray photographs from single crystals. Xray diffraction analysis is the method by which multiple beams of xray create a threedimensional picture of the density of electrons of any crystalline structure. The purpose is to identifywith a high degree of certaintythe composition of the molecules, on an atomic XRay Diffraction Analysis (XRD) investigates crystalline material structure, including atomic arrangement, crystallite size, and imperfections. Intertek XRD analysis and expertise is available for a very wide range of sample types and applications. Advanced Methods in Xray Powder Diffraction, is designed for the experienced user and focuses on computerbased methods of qualitative and quantitative phase analysis, as well as crystal structure analysis and refinement. Xray diffraction is a nondestructive analytical technique which can yield the unique fingerprint of Bragg reflections associated with a crystal structure. One can regard a crystal structure as being built of layers, or planes, which each act as a semitransparent mirror. Xray diffraction (XRD) is the only laboratory technique that reveals structural information, such as chemical composition, crystal structure, crystallite size, strain, preferred orientation and layer thickness. XRay Diffraction (XRD Analysis) Powder XRD provides detailed information on the crystallographic structure and physical properties of materials and thin films. The sample is irradiated with a beam of monochromatic xrays over a variable incident angle range. Xray diffraction is the elastic scattering of xray photons by atoms in a periodic lattice. The scattered monochromatic xrays that are in phase give constructive interference. The scattered monochromatic xrays that are in phase give constructive interference. The new D8 ENDEAVOR is an advanced Xray Diffraction (XRD) system for powder applications in industrial process optimization and quality control. The system can be used stand alone in a multiuser environment, or integrated into a laboratory environment for fully automated operation. Xray diffraction (XRD) is a powerful nondestructive technique for characterizing crystalline materials. It provides information on crystal structure, phase, preferred crystal orientation (texture), and other structural parameters, such as average grain size, crystallinity, strain, and crystal defects. The scattering of xrays by crystal atoms, producing a diffraction pattern that yields information about the structure of the crystal. Xray diffraction n (General Physics) the scattering of Xrays on contact with matter, resulting in changes in radiation intensity, which is used for studying atomic structure xray diffraction n. Xray diffraction (XRD) is one of the most important nondestructive tools to analyze all kinds of matterranging from fluids, to powders and crystals. From research to production and engineering, XRD is an indispensable method for materials characterization and quality control. Our Pledge H M Analytical Services has over 30 years experience in Xray diffraction. With our stateoftheart equipment, we will strive to apply our experience and knowl Xray diffraction (XRD) is a tool for characterizing arrangement of atoms in crystals and distances between crystal faces. This can be used to identify atoms and the crystalline form. What is Xray diffraction and how it can be used to measure stresses from crystalline materials. What is Xray diffraction and how it can be used to measure stresses from crystalline materials. Powder Xray diffraction patterns are the fingerprint of all crystalline substances. The technique is a rapid and powerful tool for identification of all crystalline compounds, and it is especially valuable in the presence of polymorphs or quasiisochemical compounds, where chemical techniques cannot be applied. XRay Diffraction, frequently abbreviated as XRD analysis, is a nondestructive test method used to analyze the structure of materials. The XRD technique, by way of the study of the crystal structure, can be used to identify the crystalline phases present in a. Prinsip dari alat XRD (Xray powder diffraction) adalah sinar X yang dihasilkan dari suatu logam tertentu memiliki panjang gelombang tertentu, sehingga dengan memfariasi besar sudut pantulan sehingga terjadi pantulan elastis yang dapat dideteksi. Maka menurut Hukum Bragg jarak antar bidang atom dapat dihitung dengan data difraksi yang dihasilkan pada besar sudut sudut tertentu. The resolution of an Xray diffraction detector is determined by the Bragg equation: where d is the resolution of the detector, lambda is the incident xray wavelength, and theta is the angle of diffraction. reflection and xray diffraction as synonyms. Let us consider an xray beam incident on a pair of parallel planes P1 and P2, separated by an interplanar spacing d. The two parallel incident rays 1 and 2 make an angle (THETA) with these planes. xray diffraction The scattering of xrays by crystal atoms, producing a diffraction pattern that yields information about the structure of the crystal. Xray diffraction is used in xray crystallography. I performed Xray Diffraction test on the shell powder and silane treated shell powder. Can u suggest, how to infer details from the XRD results. If possible kindly suggest some XRD analysis tool. Xray diffractometers can nondestructively analyze matter in regular atmospheric conditions. Qualitative analysis of matter, lattice constant determination, stress measurement, and other operations are possible. Quantitative analysis can also be performed from peak area calculations..
-
Related Images: